ZIMSEC O Level Business Studies Notes: Marketing: The Product Life Cycle
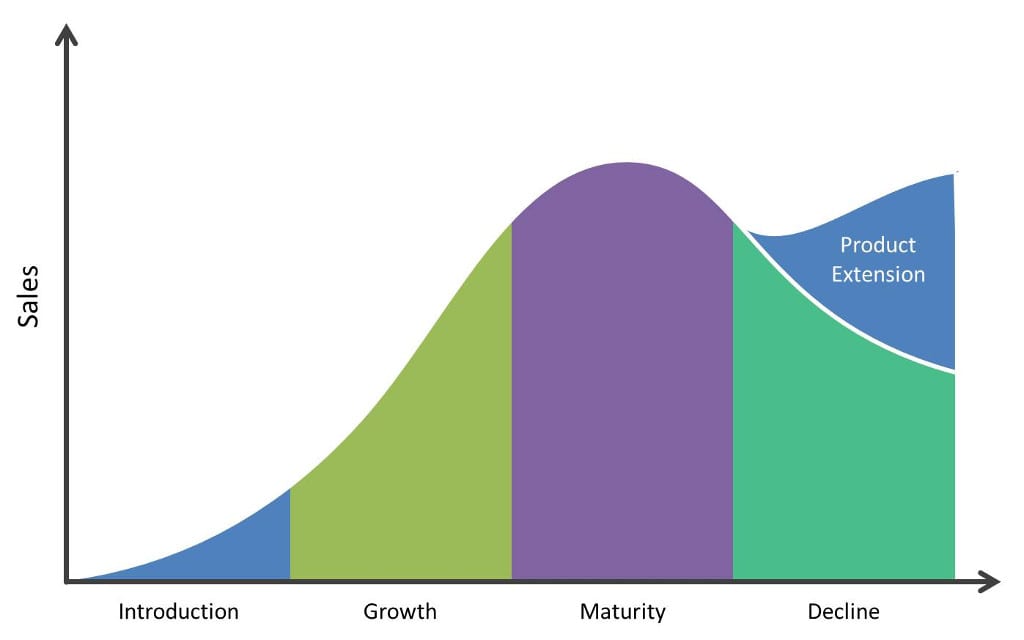
- The term product life cycle is used to describe the phases through which a product passes from its introduction to decline
- It is a basic fact in business that all products introduced go through a number of phases from their introduction to their eventual elimination
- Generally a product goes through following stages:
- Product Development phase
- Launch or Introduction phase
- The growth phase
- Maturity phase
- Saturation
- Decline
- Extension or Elimination
- The four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, decline are deemed the most important at Ordinary level
Introduction
- Is characterized by:
- Low sales volumes
- High costs due to for example high promotional costs
- Heavy promotional spending
- High risks of the product failing
- Promotions aim mainly to create awareness e.g. informing the potential market that the product exists
- During this stage only innovators are buying the product
- The product is unlikely to be profitable at this stage
- high production cost due to limited volumes being made
Growth
- Higher sales volume
- A rise in profits and sales volume
- A fall in costs due to economies of scale resulting in increased profits
- The product is bought by early adopters
- Promotions are still aimed at creating awareness
- Product penetrates the market
Maturity
- Sales continue to rise but at a reduced rate when compared to the growth phase
- The product is now being purchased by the majority
- The business’s promotional strategy are aimed at creating brand preference
- The business is also concerned with retaining its market share
- Promotion is mainly persuasive and comparative
Saturation
- Sales have leveled off rather than rise at rising at a slow rate as in the maturity phase
- Most people in the potential market have already bought the product if its a one off product or if not people are buying it at a steady unchanging rate
Decline
- Sales and profits decline
- Substitutes appear and the product becomes obsolete
- The firm can either eliminate the product or employ extension strategies
Extension
- This where strategies meant to rejuvenate the product are employed
- Popular extension strategies include:
- Changes in the product itself e.g. add more Memory to a smartphone
- Changing it’s packaging
- Changing the way it is promoted
- Changing the channels of distribution
Importance of the product life cycle
- Enables the business to map out the performance of the product
- Allows the business to anticipate and craft marketing strategy at each stage
- Helps with creating promotional strategies
- Helps the production department to determine the necessary production volumes
To access more topics go to the O Level Business Notes